A Government Tax Per Unit of Output Reduces Supply.
The Effect of Tax on the Demand Curve. The two types of indirect tax include Ad valorem tax and Specific tax.
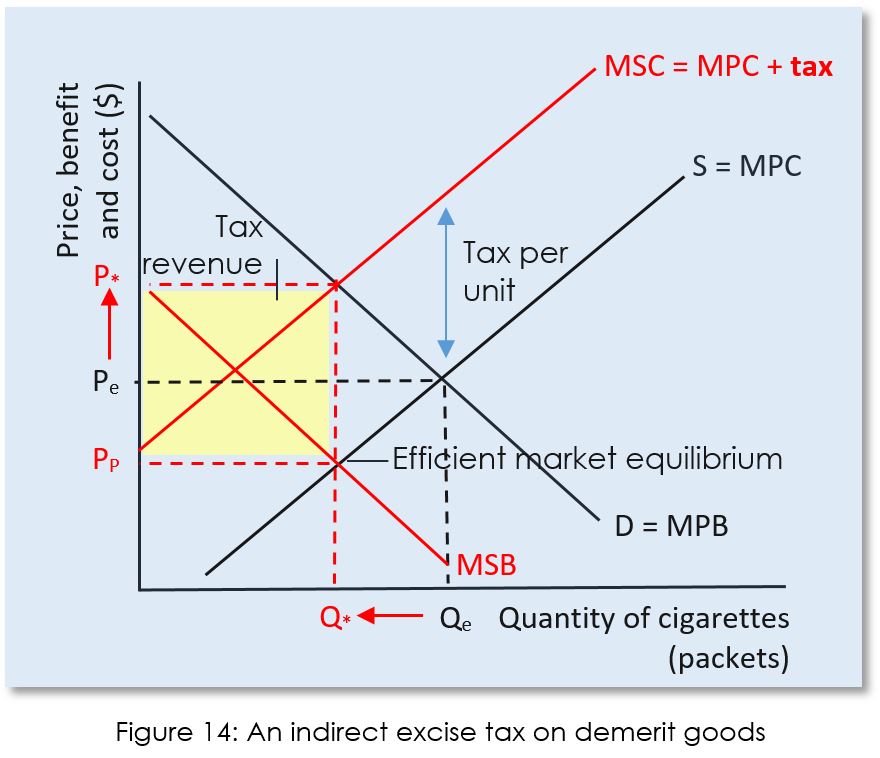
Externalities Ap Microeconomics Ap Microeconomics
Tax on Output or output tax.

. The producer has to pay the tax to the government. The supply curve for each of these two goods is identical as you can see on each of the following graphs. 1 per unit is imposed on cigarettes.
An alternative tax is an ad valorem tax which is stated as a given percentage of the selling price. With the imposition of a 100 tax per unit the price buyers pay is 1 more than the price suppliers receive. Business Economics QA Library The government is considering levying a tax of 100 per unit on suppliers of either leather jackets or smartphones.
As it has a direct relationship with the output level it is considered an increase in variable costs. The market will clear. Tax shifts demand to the left and raises equilibrium meaning higher prices.
Achieving productive efficiency but not allocative. Specific taxes are commodity taxes like excise duty and sales tax. Jeff supply and demand tax One form of government intervention is the introduction of taxes.
What price will the buyer pay. This preview shows page 1 - 4 out of 4 pages. Qs -42P-t In equilibrium Qd Qs 66-3P -42P-t 66-3P -42P-2t -3P-2P -4-2t-66 -5P -70-2t 5P 702t P 142 5t.
Because of the increased cost we generally see a reduction in the quantity of goods and. False If market demand increases and market supply decreases the change in equilibrium price is unpredictable without first knowing the exact magnitudes of the demand and supply changes. If market demand increases and market supply decreases the change in equilibrium price in unpredictable without first knowing the exact magnitudes of the demand and supply changes.
The government pays a subsidy of 5 per unit produced. If the product produces a positive externality a per-unit tax will increase deadweight loss. The least efficient firms will be forced to exit the market.
They also affect a consumers willingness to buy a product or service. The government imposes a tax of 1 per unit. Deadweight loss of taxation measures the overall economic loss caused by a new tax on a product or service.
Excise duty are levied on production while sale tax on sales. The demand for leather jackets is shown by D on the first graph and the demand for smartphones is shown by Ds on the. A government tax per unit of output reduces supply.
A government tax per unit of output reduces supply. Ii How would a per unit sales tax t affect this equilibrium and comment on how the tax is shared between producers and consumers Sales tax reduces suppliers price by t P-t Supply curve becomes. To model the price-quantity impacts of a subsidy we can shift the demand curve upward by the amount of the per-unit subsidy payment.
Farmers would thus receive the market price of 3 plus a government payment of 1 per unit. Subsidies When the government grants a subsidy to the producers of a good or service the supply curve will shift to the right by the vertical distance of the subsidy. Suppose the government imposes a tax of 1 per unit to reduce widget consumption and raise government revenues.
This is an example of urn specific tax. In this case the new supply curve will be. A government tax per unit of output reduces supply False A decrease in supply of X increases the equilibrium price of X which reduces the damand for X and automaticallly returns the price of X.
Taxes increase government revenue. A government tax per unit of output reduces supply. For downward sloping demand and upward sloping supply curves the government expenditure used to pay for a subsidy program exceeds the sum of the changes in producer and consumer surplus.
The market will clear. For example VAT in the UK is 20 which is then added onto the original price. In this case firms pay a certain amount for each unit of output produced.
Imposition of a Specific Tax. The effect of taxes on supply and demand. Taxes are typically introduced to increase government revenue but they also have the effect of raising the cost of goods and services to the consumer.
Supply and demand are forces that affect a businesss willingness to sell and the prices it charges. A subsidy is an amount of money given directly to firms by the government to encourage production and consumption. The effect of a specific per unit subsidy is to shift the supply curve vertically downwards by the amount of the subsidy.
1 must be paid. If for example a crop had a market price of 3 per unit and a target price of 4 per unit the government would give farmers a payment of 1 for each unit sold. Taxes and subsidies can play a significant role in how much of a product a business will produce for consumers to purchase.
This is due to the fact that as the price of the goodservice. The tax will alter the equilibrium price and quantity but there will be no excess demand or excess supply. It analyses the decrease in production and the decline in demand caused by the.
Can regulate monopoly through taxation. Question 2 of 50 10 10 Points If an economy produces its most wanted goods but uses outdated producti A. If the product produces a negative externality a per-unit tax will reduce deadweight loss.
Shifting supply to the left means a lower quantity is supplied this means that the market size shrinks. This mean that for each unit sold a tax of say Re. A unit subsidy is a specific sum per unit produced which is given to the producer.
Ad valorem taxes are shown by two supply lines that get further and further away from each other. What amount per unit will the seller receive. For example a tax of say Re.
The subsidy will alter the equilibrium price and quantity but. What will the new equilibrium quantity be. Can levy a tax per unit of output Specific Tax or impose a lump sum tax irrespective to its output.
Ad valorem taxes are percentages which are added to certain products. A government tax per unit of output reduces supply. Tax Incidence and Price Elasticity of Demand and Supply HL If a good with inelastic demand is taxed the.
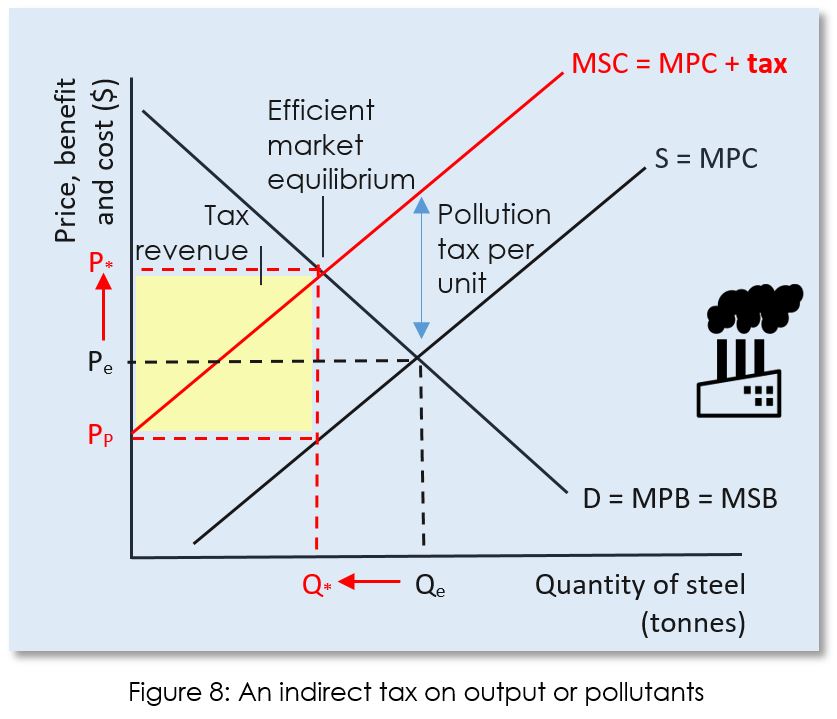
Externalities Ap Microeconomics Ap Microeconomics
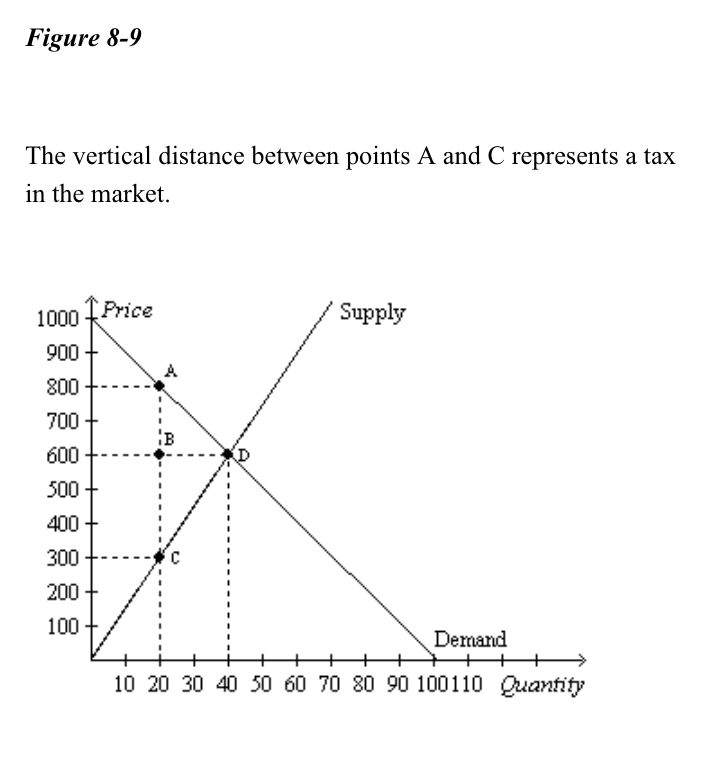
Econ 101 Ch 8 Flashcards Chegg Com

4 7 Taxes And Subsidies Principles Of Microeconomics

4 7 Taxes And Subsidies Principles Of Microeconomics
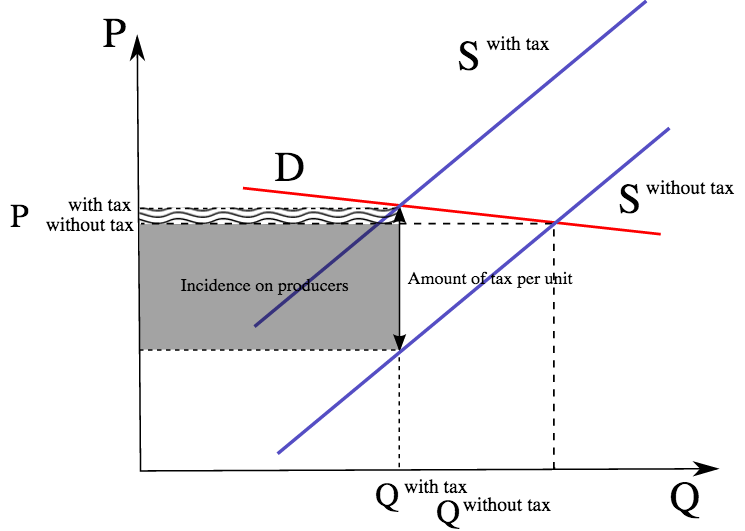
Reading Tax Incidence Macroeconomics
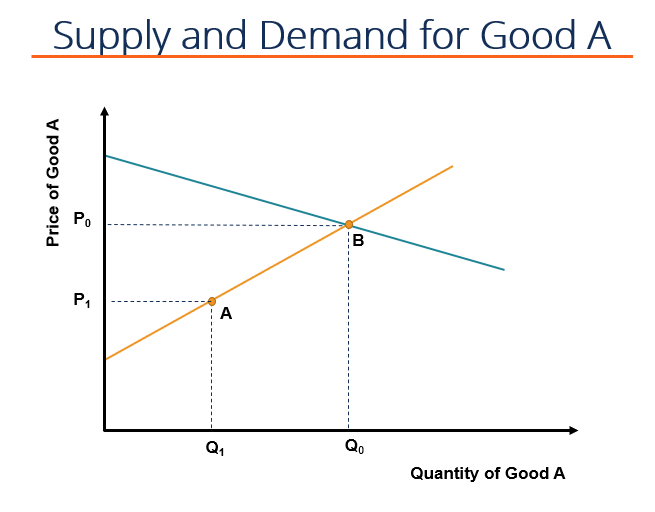
Excise Tax Overview And How It Affects The Price And Quantitiy Of Goods

Irrigation Subsidies And Their Externalities Sciencedirect
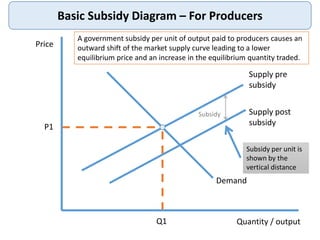
Government Intervention Subsidies

4 7 Taxes And Subsidies Principles Of Microeconomics

4 7 Taxes And Subsidies Principles Of Microeconomics







Comments
Post a Comment